Light Emitting Diodes, LEDs, are a special kind of diode.
Without going into the specifics, a diode is a semiconductor that only allows current to flow through it in one direction.
LEDs also only allow current to flow in one direction. However, they are different because they emit light as current flows through.
Because LEDs are diodes and current can only flow through an LED in one direction, they all have two different legs: the anode and cathode.
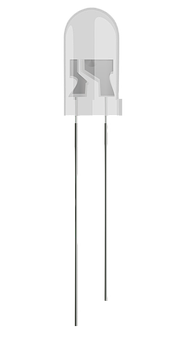
Cathode on the right
Source: pixabay.com
The anode is the positive terminal. It is the longer leg of the LED and must be connected to the positive terminal of the circuit’s power source.
The cathode is the negative terminal. It is the shorter leg of the LED and must be connected to ground, or the negative terminal of the circuit power source.
If the LED is connected to the circuit in reverse, with the cathode at the positive terminal and the anode at the negative terminal, no current will flow through the circuit. This is because LEDs are diodes and diodes are meant to only allow the flow of current in one direction and stop the flow of current in the opposite direction.
These are the schematic symbols for diodes and LEDs:
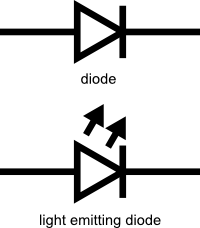
The LED’s symbol is almost the same as the diodes because it is a diode. However, there are two arrows that point away from the LED, showing that it emits light.




