Published by Raymond Alvin on 1/7/21
Source: sparkfun.com
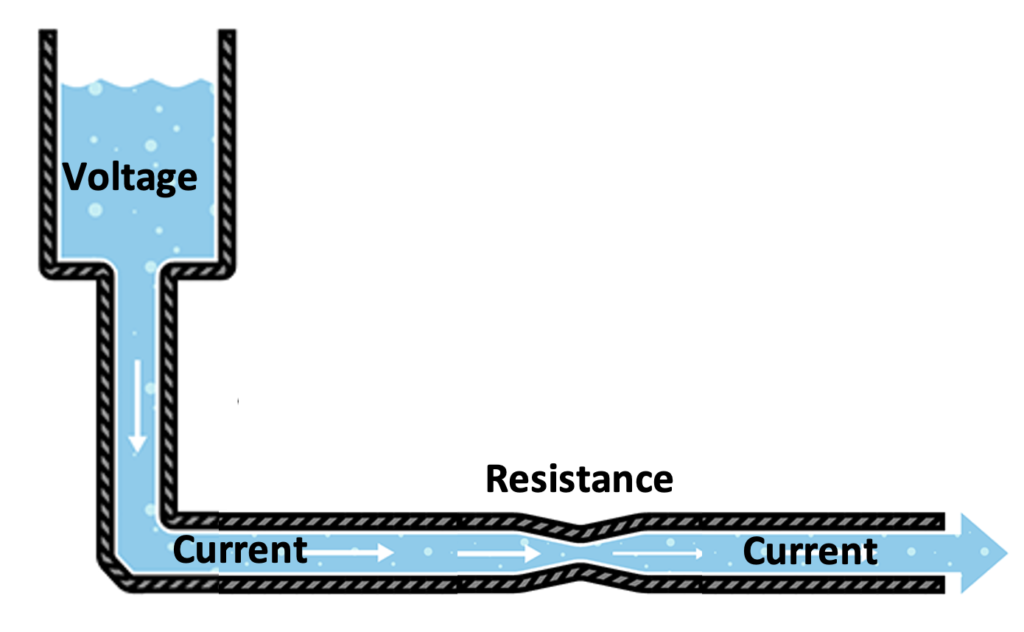
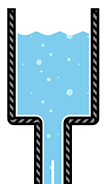
Voltage (V)
Voltage is the potential difference in a circuit.
It is like potential energy or electricity that can go through a circuit.
It is possible that all of the voltage supplied to a circuit will go through the circuit. However, this will cause a short circuit and most circuits have resistance, which stops all of the voltage from going through at once.
Voltage is analogous to a water tank. Lots of water is stored in the tank just like voltage is stored in a battery. The voltage may all go through a circuit at once, causing a short circuit. Similarly, the water may all go through the pipe at once, causing a pipe burst. To prevent this, resistance is added to a circuit just and pipe diameters are reduced to control water and voltage.
Source: sparkfun.com
Voltage is measured in Volts.
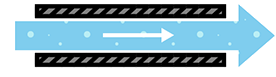
Current (I)
Current is the actual kinetic energy or electricity flowing through a circuit.
Voltage is like a theoretical number and estimate of what can flow through a circuit but current is what actually flows through a circuit.
Current is analogous to the water that is flowing through the pipe. It is less than the water in the water tanks and controlled by the diameter of the pipe, just like how current is controlled by resistance.
Pipe (Current)
Source: sparkfun.com
Current is measured in Amperes (Amps).
Resistance (R)
Resistance is the force that reduces current.
Resistance is analogous to a constriction/reduction in the diameter of a pipe. With a smaller diameter, less water can flow through the pipe just like how less current can flow through a circuit with more resistance.

Constriction In A Pipe (Resistance)
Source: sparkfun.com
Resistance is measured in Ohms.
Ohm’s Law
V = IR
Voltage = (Current)(Resistance)
Ohm’s law can be used to calculate the voltage, current, or resistance in a circuit. If two values are known, the other can be found by rearranging the equation.
I = V/R
Current = (Voltage)(Resistance)
R = V/I
Resistance = (Voltage)(Resistance)




